Introduction
WEB-T – eTranslation multilingual is a WordPress plugin for automated website content translation. Your website must be monolingual and must have WordPress version 3.1.0 or greater. Using it together with other multilingual website solutions can cause unexpected usage or technical issues.
How it works
WEB-T– eTranslation multilingual translates the webpage content when selecting language from the language selector. You can also pre-translate the existing website content all at once in WEB-T– eTranslation multilignual settings > Advanced> Manage translations. All translations are saved into your database, allowing you to edit them via translation editor.
- Install the plugin.
- Get MT provider access
- Configure translation provider in plugin settings.
- Configure translation languages and domains.
- Translate your website either one page at a time, or pre-translate all content at once.
- Use translation editor to improve translated texts. The corrections will instantly appear on your website.
| Please note: Websites using WEB-T plugin with eTranslation integration enabled must be published and accessible online from eTranslation service. Translation with eTranslation will not work otherwise. |
Install plugin
From WordPress plugin directory
The plugin is available for download at the WordPress plugin directory: https://wordpress.org/plugins/etranslation-multilingual/
To install the plugin:
- Open the WordPress dashboard.
- Open the Plugins section.
- At the top of the page, click Add new.
- Search for “web-t - etranslation multilingual” and find the plugin
- Click Install Now
- After installation is completed, click Activate
Manually from ZIP file
To install the plugin:
- Open the WordPress dashboard.
- Open the Plugins section.
- At the top of the page, click Add new.
- Click Upload Plugin.
- Click Choose file and upload the plugin .zip file. ZIP file can be downloaded here: https://website-translation.language-tools.ec.europa.eu/solutions/web-t-wordpress_en
- Click Install Now.
- When the installation is complete, click Activate Plugin.
Alternatively, upload the unzipped plugin folder to the /wp-content/plugins/ directory.
Overview
In plugins’ settings you will find:
- General – for setting translation languages, language switcher appearance, language display settings and using subdirectory for the default language.
- Translate site – for opening translation editor.
- Automated translation – for setting translation provider, blocking crawlers, chaning machine translation notice visibillity.
- Advanced – formanagin translations (pre-translate, delete), troubleshooting options, excluding content for translation, adding additional SEO tags for translation, debug and other options.
In translation editor you will find:
- Visual editor – for editing visible and SEO translations.
- String translation – for editing gettext string (theme and plugin strings) and email translation.
Configure translation provider
Before you continue:
You must have an eTranslation or WEB-T compatible translation provider account.
You have obtained eTranslation API credentials or Base URL & API key from your translation provider.
To configure the translation provider:
- On the WordPress dashboard, open the Plugins section
- Find WEB-T – eTranslation multilingual.
- Click Settings.
- In the Automated Translation tab, enable automated translation.
- Select the translation engine. You can either use eTranslation or a custom translation provider.
- Enter the credentials for your translation provider:
- Enter the username and password for eTranslation
- or base URL and API key for custom provider.
- At the bottom of the page, click Save Changes.
Configure translation languages and domains
To configure the translation languages:
- On the WordPress dashboard, open the Plugins section.
- Find WEB-T eTranslation multilingual.
- Click Settings.
- In the General tab, set the default language of your website.
- In the All Languages section, select the language(-es) and domains, and click Add.
- At the bottom of the page, click Save Changes.
The order of the languages will determine the order in which they appear in the language switcher; change it by dragging.
Verify plugin is configured correctly
To verify that the plugin is configured correctly:
- Open your website.
- At the top of the page, look for a floating language selector.
- Select a language.
- The page will be reloaded and automatically translated into the selected language.
- A translation notice bar will appear.
Change language switcher appearance
The language switcher has three options: shortcode, menu item, floating language selection.
In this section:
Floating language switcher
The default is a floating language selection at the top right corner of the page.
To change the floating language menu appearance:
- In the plugin’s settings, open the General tab.
- At the bottom of the page, find the Language switcher section.
- Under Floating language selection, select a theme.
- Click Save Changes.
Change floating language switcher position
Language switcher can be displayed at: top right, top left, bottom right, bottom left positions.
To change the position the floating language switcher appears in:
- In the plugin’s settings, open the General tab.
- At the bottom of the page, find the Language switcher section.
- Under Floating language selection, select the position.
- Click Save Changes.
Disable default floating language switcher
If you are using shortcode menu or menu item for switching languages, you can hide the default floating language switcher.
To disable the floating language selection:
- In the plugin’s settings, open the General tab.
- At the bottom of the page, find the Language switcher section.
- Unselect Floating language selection.
- Click Save Changes.
Shortcode language switcher
Shortcode switcher can be added to any page by using [language-switcher] shortcode.
Add shortcode language switcher to a page
To add a shortcode language switcher to a single page:
- In the editor open the page you want to edit.
- Add a text block and type [language-switcher].
- At the top of the page, click Update.
Add shortcode language switcher to a header, footer, or sidebar
To add a shortcode language switcher to footer, header, or sidebar:
- On the WordPress dashboard, open Appearance > Widgets.
- Find the header/footer/sidebar widget.
- Click “+” and add a text block.
- Type [language-switcher].
- At the top of the page, click Update.
Languages as menu items
To add the language switcher to any menu:
- On the WordPress dashboard, open Appearance > Menus.
- Create a new menu or edit an existing one.
- Under Add menu items, expand Language switcher.
- Select the languages.
- Click Add to menu.
- Select display location of the menu.
- Save changes.
To change how the languages are displayed:
- In the plugin’s settings, open the General tab.
- At the bottom of the page, find the Language switcher section.
- Under the language switcher you are using, select the language appearance.
- Click Save Changes.
Customize machine translation notice bar
By default, machine translated pages have a notice bar displayed at the top of the page, informing the visitor that the page is machine translated. It also provides an option to revert the page to original language. The message itself is also machine translated .
To edit the translation notice bar message:
- Open the Translation editor.
- Hover over the notice bar and click .
- Edit the translation.
- At the top of the page, click Save translation.
To display the notice in English for website visitors:
- In the plugin’s settings, open the Advanced tab.
- Find the Exclude strings section.
- Under Exclude selectors only from automated translation, add “.translationnotice” to the selectors.
- At the bottom of the page, click Save Changes
To disable the notice bar completely:
- In the plugin’s settings, open the Automated translation tab.
- Next to Show machine translation notice, select “No”.
Content translation and editing
Translation editor allows selecting and translating text found in the current page. Translation is done on a string by string basis. For example, a sentence with a link as a part of it will be treated as separate strings. To edit translations from different pages you must first open the given page.
In this section:
- Open Translation editor
- Translate a single page or article
- Translate all pages and posts (Pre-translation)
- Edit Automated translations or add manual
- Merge text into blocks
- Translate SEO meta data
- Display different image for each language
- Translate Gettext strings
- Translate emails
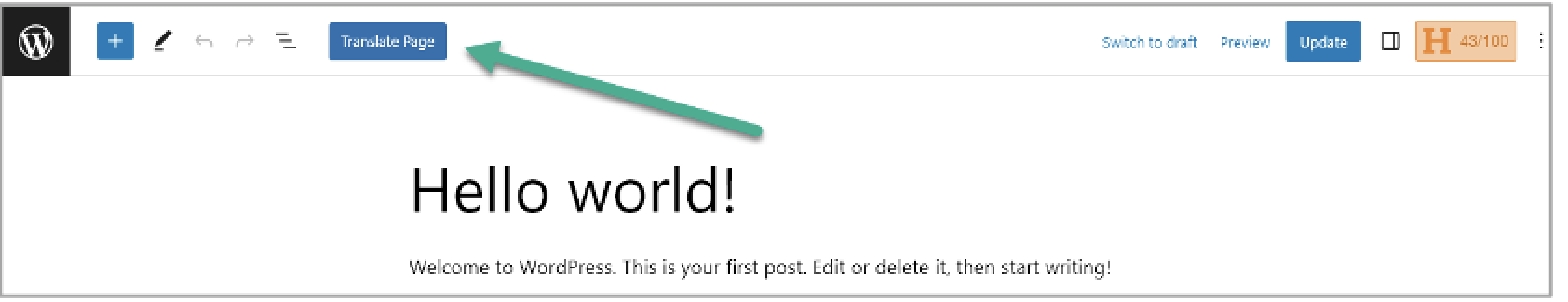
Open Translation editor
To open the translation editor:
- In the plugin’s settings, click Translate site tab.
or
- At the top of the page, on the WordPress admin toolbar, click Translate Page.
Translate a single page or article
To translate a single page or article:
- Open the page.
- Select a language from language switcher.
- The page will be reloaded and automatically translated into the selected language.
- A translation notice bar will appear.
To translate a single page in Translation editor:
- Open the Translation editor.
- On the Visual editor tab, select the translation language.
- Wait for translation to be finished.
Translate all pages and posts (Pre-translation)
To translate all pages and posts:
- In the plugin’s settings, open the Advanced tab.
- Under Manage translations, click Translate all.
Edit Automated translations or add manual
To edit Automated translation or add manual translations:
- Open the Translation editor.
- On the Visual editor tab, select the translation language.
- Select the string to translate:
- In the side panel, select from the dropdown menu.
or - Find the text string on the page, hover and click .
- In the side panel, select from the dropdown menu.
- Edit the translation.
- At the top of the page, click Save translation.
Merge text into blocks
To merge text into larger blocks:
- Find the text you want to merge.
- Hover and click .
Translate SEO meta data
To edit SEO meta data translations or add manual translations:
- Open the Translation editor.
- In the side panel, select the translation language.
- Select the SEO string to translate.
- Edit the translation.
- At the top of the page, click Save translation.
To enable additional SEO string translation see "Additional SEO meta tags".
Display different image for each language
To change an image:
- Open the Translation editor.
- Find the image on the page, hover and click .
- In the side panel, click Add media.
- Select an image.
- At the top of the page, click Save translation.
Translate Gettext strings
Theme and plugin translations such as form fields or popups can be managed on the Gettext tab of String translation. First click “Rescan plugins and theme settings” to see all the strings, otherwise only the ones that already been displayed when visiting the website will be found in the table. You can filter strings by translation status, domain or text.
To view, edit or add manual translations gettext strings:
- Open the Translation editor
- In the side panel, click String translation.
- Filter table by language.
- Hover over the original string and click Edit.
- Edit the translation.
- At the top of the page, click Save translation.
Translate emails
Woocommerce emails will be sent in the customer’s preferred language. To make sure every email string is translated correctly and make edits, you can search for each string with “Search email strings”. If you don’t find the string in the list check “Gettext” tab as well.
To view, edit Automated translation or add manual translations of emails:
- Open the Translation editor.
- In the side panel, click String translation.
- Select Emails tab.
- Filter table by language.
- Hover over the original string and click Edit.
- Edit the translation.
- At the top of the page, click Save translation.
If you are not seeing your emails, click Rescan plugins and theme for strings.
FAQ
How to change the Automated translation engine and update translations?
To change the Automated translation engine and update the translations for all the website content:
- Delete the previous translations, see "How to delete translations"?
- Configure the new languages, see "Configure translation provider" and "Configure translation languages and domains".
- Translate the content, see "Content translation and editing".
How to delete translations?
To delete all the translations made with WEB-T plugin:
- In the plugin’s settings, open the Advanced tab.
- Under Manage translations, click Delete translations.
How to exclude some of the content from translation?
To exclude content from translation:
- In the plugin’s settings, open the Advanced tab.
- Find the Exclude strings section.
- Under Exclude Gettext Strings, add your Gettext strings
or
- add HTML selectors under Exclude selectors from translation.
- At the bottom of the page, click Save Changes.
How to exclude some of the content from Automated translation?
To exclude content from Automated translation:
- In the plugin’s settings, open the Advanced tab.
- Find the Exclude strings section.
- Under Exclude strings from Automated translation, add the strings (names, technical jargon etc.).
- At the bottom of the page, click Save Changes.
How to exclude certain pages from translation?
To exclude paths from translation:
- In the plugin’s settings, open the Advanced tab.
- Find the Exclude strings section.
- Under Do not translate certain paths, select between “Exclude Paths from Translation” and “Translate Only Certain Paths”.
- Add the paths.
- At the bottom of the page, click Save Changes.
Can I skip dynamic content detection?
To skip dynamic content detection:
- In the plugin’s settings, open the Advanced tab.
- Find the Exclude strings section.
- Under Exclude from dynamic translation, add the element selectors.
- At the bottom of the page, click Save Changes.
Does the extension translate images?
Images have to be localized by the user themselves and added into the translated pages.
Will the translation affect website load times?
There is no noticeable difference in load times between translated content and regular articles. If a page is not pre-translated the visitor will have to wait for the translation.
Troubleshooting
Translation doesn’t work
Websites using WEB-T plugin with eTranslation integration enabled must be published and accessible online from eTranslation service. Translation with eTranslation will not work otherwise.
To fix this, publish these websites online and make sure these URLs are accessible from outside (e.g. by making HTTP POST requests):
{{WEBSITE_URL}}/wp-json/etranslation/v1/document/destination/123Translation is slow
Translation speed is translation provider dependant. Systems offered by eTranslation are used by a huge number of users. They may be slow at time due to the heavy work load.
First time the content of any page is loaded it will take some time to translate it. The translation will be saved and returned instantly the next time.
Translation contains errors
Machine translation cannot fully substitute human translators. The translations have to be reviewed and edited by a human. The quality of the translation depends on the machine translation engine and provider.
Some functionality doesn’t work in the translated page
HTML might be invalid or poorly formatted in the used WordPress theme or other plugins. The plugin can try to fix some of the HTML.
To try Automatedally fixing the HTML:
- In the plugin’s settings, open the Advanced tab.
- At the top of the page, find the Troubleshooting section.
- Next to Fix broken HTML, check “Yes”.
Dynamically loaded content is missing in the translation
If content inserted using JavaScript is missing in the translation, the plugin can show the dynamic content in the original language before the translation is finished.
To try Automatedally fixing the HTML:
- In the plugin’s settings, open the Advanced tab.
- At the top of the page, find the Troubleshooting section.
- Next to Fix missing dynamic content, check “Yes”.
Post or page titles are empty or broken in the translated page
To disable post container tags for post titles:
- In the plugin’s settings, open the Advanced tab.
- Find the Debug section.
- Next to Disable post container tags for post title, check “Yes”.
Filter Gettext wrapping from post content, titles or meta
To filter Gettext wrapping such as #!trpst#trp-gettext from updated or future posts:
- In the plugin’s settings, open the Advanced tab.
- At the top of the page, find the Troubleshooting section.
- Next to Filter Gettext wrapping from post content and title, check “Yes”.
or
- Next to Filter Gettext wrapping from post meta, check “Yes”.
- At the bottom of the page, click Save Changes.
(!) We recommend making a database backup before enabling these settings.
Settings
General
Default Language – select the original language the website is written in. By default set to the language that is selected when installing WordPress.
All Languages – select languages that you want to translate into.
Native language name – display languages in their native names. Selecting “No” they will be displayed in English.
Use a subdirectory for the default language – Select “Yes” to add the language slug to the URL for the default language. The URL will be changed from www.example.com to www.example.com/en/.
Force language in custom links – Select “Yes” to force custom links without language encoding to add the language slug to the URL for the default language. For example, if your website URL is www.example.com and the default language is English, then a custom link to the home page would be www.example.com/en/ even if the link does not include the language slug.
Language Switcher – Language switcher is a menu that the visitors will use for selecting the language of the website. You can customize the it is displayed, please see: "Change language switcher appearance".
Translate Site
Clicking on this tab will open the Translation Editor in the frontend of your website, where you can start translating your website, please see: "Open Translation editor".
Automated translation
Enable Automated Translation – Select “Yes” to enable and configure Automated translation. Please see: "Configure translation provider".
Translation Engine – Select and configure Automated translation provider. Please see: "Configure translation provider".
Block Crawlers – Enabling this option will prevent crawlers from triggering the Automated translation of your website.
Log machine translation queries – Only enable this setting for testing purposes. It can affect your website's performance. All records are stored in the wp_etm_machine_translation_log database table.
Show machine translation notice – Select “No” to hide the notice about Automated translation. Please see: "Customize machine translation notice bar".
Advanced settings
Troubleshooting
Fix missing dynamic content - This option may help if you're missing content on translated pages that was inserted using JavaScript. It works by showing the content in the original language for a moment before the translation is finished. This can help you identify the missing content so you can fix the problem.
Disable dynamic translation - This option will stop the translation of content that is displayed dynamically using JavaScript. However, content that is loaded from the server using AJAX or the HTML page itself will still be translated.
Fix broken HTML - This option tries to fix broken HTML on translated pages.
Filter Gettext wrapping from post content and title - This option removes the gettext wrapping from all new post content and titles. This wrapping, such as #!trpst#trp-gettext, is used to identify text that needs to be translated. However, it does not affect any previously saved post content.
Delete translations - Removes all translations stored by this plugin from database, both Automated and manually edited.
Exclude strings
Exclude gettext strings - This option allows you to exclude certain strings from being translated as Gettext strings. This can be useful if you want to prevent certain strings from being translated, such as technical terms or strings that are used as keys in options.
To exclude a string, you need to enter the string and the domain (if applicable). The domain is the name of the group of strings that you want to exclude. If you leave the domain empty, matching strings from all domains will be excluded.
After entering the string and domain, click the Add button to add the string to the list of excluded strings. To remove a string from the list, click the Remove button.
Exclude strings from Automated translation - This option allows you to exclude certain strings from being machine translated. This can be useful if you want to prevent certain strings from being machine translated, such as technical terms or strings that are used as keys in options. Paragraphs containing these strings will still be translated except for the specified part.
Exclude from dynamic translation - This option allows you to prevent certain strings from being translated dynamically using JavaScript. This means that these strings will only be translated on the server side, if possible. To exclude a string, you need to enter a JavaScript selector that matches the HTML node that contains the string. For example, you could use the selector .my-selector to exclude all strings that are found in HTML nodes with the class my-selector.
Exclude selectors from translation - This option allows you to prevent certain strings from being translated. This means that these strings will not be translated if they are found in HTML nodes that match the selectors you enter. To exclude a string, you need to enter a JavaScript selector that matches the HTML node that contains the string. For example, you could use the selector .my-selector to exclude all strings that are found in HTML nodes with the class my-selector. You can use any type of JavaScript selector to exclude strings, except for the not() selector and the double attribute selector [attribute1][attribute2].
Do not translate certain paths - Choose which paths can be translated.
- Exclude paths from translation: This mode allows you to specify which paths should not be translated. For example, you could exclude the homepage by using the rule {{home}}.
- Translate only certain paths: This mode allows you to specify which paths should be translated. For example, you could translate all pages that start with the path /some/path/ by using the rule /some/path/.
Additional SEO meta tags
Meta tags with string type value - This option allows you to add aditional SEO meta tags that should be translated. Add translatable SEO meta tags which contain string type value.
Meta tag name examples:
- description
- og:title,
- og:type,
- og:site_name
- og:description,
- twitter:title,
- twitter:description,
- twitter:card
- twitter:label1
- twitter:data1
Meta tag attribute (attribute that holds the meta tag name) examples:
- property
- name
Meta tags with image type value - Add translatable SEO meta tags which contain image type value.
Meta tag name examples:
- og:image
- og:image:secure_url
- twitter:image
Meta tag value examples:
- property
- name
Meta tag value will be retrieved from ‘content’ attribute for both string and image type meta tags.
Debug
Disable post container tags for post title - This option prevents the post title from being indexed by search engines in translated languages. This can be useful if the post title doesn’t allow HTML and would break the page.
Disable post container tags for post content - This option prevents the post content from being indexed by search engines in translated languages. This can be useful if the post content doesn’t allow HTML and would break the page.
Disable translation for gettext strings - This option disables the translation of gettext strings. If you have already translated the strings in your themes and plugins using the .po/.mo translation file system, you can disable the translation of these strings with the plugin. This can improve the page load performance of your site in some cases. However, you will no longer be able to edit these translations with WEB-T plugin, and you will not benefit from the Automated translation of these strings.
Show regular strings tab in String Translation - This option adds a new tab to the String Translation interface that allows you to edit translations of strings that were entered by users.
Optimize eTranslation Multilingual database tables - This feature allows you to clean up your database tables by removing duplicate rows, untranslated links, and CDATA.
Miscellaneous options
Remove duplicate hreflang - Select the hreflang tag(s) that will be visible on your website: Country Locale (en-UK), Region Independent Locale (en), or both. By default, both the Country and the Region Independent Locale are shown (recommended).
HTML Lang Attribute Format - Modify the format of the lang attribute within the html tag to incorporate the country's regional information, if applicable.
In HTML, the lang attribute is used to indicate the language of textual content. This enables the browser to accurately display or process content, such as for styling, hyphenation, spell checking, etc.
eTranslation timeout – Seconds per single request to wait on eTranslation to send translation response when translating from frontend (not in editor/pre-translation mode).
Force slash at end of home URL - Appends a trailing slash to the home_url() function.
Translate numbers and numerals - When activated, this feature enables the translation of numbers (e.g., phone numbers) found within the text. This can be useful for displaying different contact phone numbers for each translated language on your website.
Enable the hreflang x-default tag for language - Enables the hreflang="x-default" attribute for an entire language.
Date format - Allows customization of the display format for date and time in each translated language. Utilizes the same format as WordPress date and time formatting. Note that this feature does not store translated date and time text; it merely provides finer customization options.
Show opposite language in the language switcher - Transforms the language switcher into a button that displays the available language other than the current one. This applies only when there are exactly two languages: the default language and its translation. This alteration affects both the shortcode language switcher and the floating language switcher. To implement this in the menu language switcher, navigate to Appearance → Menus → Language Switcher and select "Opposite Language."
Open language switcher only on click - Changes the behavior of the language switcher shortcode, causing it to open upon clicking rather than hovering. It can be closed by clicking on it, anywhere else on the screen, or by pressing the escape key. This adjustment exclusively applies to the shortcode language switcher.
Custom language
Custom language - This functionality becomes valuable when you're translating your website into a language that isn't included in the General Settings. It enables you to add one or more custom languages, which will then be displayed on the front end and accessible within the translation options. There is no restriction on the quantity of custom languages you can add.